1.Identification
1.1 GHS Product identifier
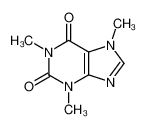
| Product name | caffeine |
|---|
1.2 Other means of identification
| Product number | - |
|---|---|
| Other names | 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-1,3,7-trimethyl- |
1.3 Recommended use of the chemical and restrictions on use
| Identified uses | For industry use only. Food additives -> Flavoring Agents |
|---|---|
| Uses advised against | no data available |
1.4 Supplier's details
| Company | MOLBASE (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
|---|---|
| Address | Floor 4 & 5, Building 12, No. 1001 North Qinzhou Road, Xuhui District, Shanghai, China |
| Telephone | +86(21)64956998 |
| Fax | +86(21)54365166 |
1.5 Emergency phone number
| Emergency phone number | +86-400-6021-666 |
|---|---|
| Service hours | Monday to Friday, 9am-5pm (Standard time zone: UTC/GMT +8 hours). |
2.Hazard identification
2.1 Classification of the substance or mixture
Acute toxicity - Oral, Category 4
2.2 GHS label elements, including precautionary statements
| Pictogram(s) |  |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statement(s) | H302 Harmful if swallowed |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| Prevention | P264 Wash ... thoroughly after handling. P270 Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. |
| Response | P301+P312 IF SWALLOWED: Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/…if you feel unwell. P330 Rinse mouth. |
| Storage | none |
| Disposal | P501 Dispose of contents/container to ... |
2.3 Other hazards which do not result in classification
none
3.Composition/information on ingredients
3.1 Substances
| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| caffeine | caffeine | 58-08-2 | none | 100% |
4.First-aid measures
4.1 Description of necessary first-aid measures
General advice
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaled
Fresh air, rest. Refer for medical attention.
In case of skin contact
Remove contaminated clothes. Rinse skin with plenty of water or shower.
In case of eye contact
First rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention.
If swallowed
Rinse mouth. Refer for medical attention .
4.2 Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayed
SYMPTOMS: Symptoms of exposure to this compound may include central nervous system stimulation, less drowsiness, less fatigue, more rapid and clearer flow of thought, decreased reaction time, affects on muscular coordination, accurate timing and arithmetic skills, nervousness, restlessness, insomnia, tremors and hyperesthesia. At higher doses, symptoms include focal and generalized convulsions, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, apnea of preterm infants, vomiting, nausea, effects on circulatory system, small decreases in heart rate, tachycardia, arrhythmias, premature ventricular contractions and vasodilation. Overdosage may cause death, emesis, convulsions, excitement, mild delirium, sensory disturbances such as ringing in the ears and flashes of light, tense and tremulous muscles, extrasystoles and quickened respiration. Continued excessive use may lead to digestive disturbances, constipation, palpitations, shortness of breath and depressed mental states. Other symptoms may include pulmonary edema, myocardial infarction, ventricular fibrillation, stomach cramps, chills, cerebral edema and hypokalemia. It may also cause rapid pulse, hallucinations, photophobia, gastroenteric distress and diuresis. Anxiety and irritability may occur. Gastric irritation, headache, fever, agitation, hyperventilation and respiratory failure may also occur. Dizziness has been reported. It may also cause irritation of the skin, eyes, mucous membranes and respiratory tract. ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: This compound is harmful by ingestion, inhalation or skin absorption. It is an irritant of the skin, eyes, mucous membranes and respiratory tract. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
4.3 Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed, if necessary
Emergency and supportive measures: Maintain an open airway and assist ventilation if necessary. Treat seizures and hypotension if they occur. Extreme anxiety or agitation may respond to benzodiazepines such as IV lorazepam. Hypokalemia usually resolves without treatment but in severe poisonings may need treatment as it can contribute to life-threatening arrhythmias. Monitor ECG and vital signs for at least 6 hours after ingestion.
5.Fire-fighting measures
5.1 Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
Use water spray, powder.
5.2 Specific hazards arising from the chemical
Flash point data for this chemical are not available; however, it is probably combustible.
5.3 Special protective actions for fire-fighters
Wear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
6.Accidental release measures
6.1 Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust. For personal protection see section 8.
6.2 Environmental precautions
Personal protection: particulate filter respirator adapted to the airborne concentration of the substance. Sweep spilled substance into covered sealable containers. If appropriate, moisten first to prevent dusting. Carefully collect remainder. Then store and dispose of according to local regulations.
6.3 Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
Sweep spilled substance into covered sealable containers. If appropriate, moisten first to prevent dusting. Carefully collect remainder. Then store and dispose of according to local regulations.
7.Handling and storage
7.1 Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. For precautions see section 2.2.
7.2 Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Separated from food and feedstuffs. Well closed.Separated from food and feedstuffs. Well closed.
8.Exposure controls/personal protection
8.1 Control parameters
Occupational Exposure limit values
no data available
Biological limit values
no data available
8.2 Appropriate engineering controls
Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
8.3 Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE)
Eye/face protection
Safety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Wear impervious clothing. The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace. Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Respiratory protection
Wear dust mask when handling large quantities.
Thermal hazards
no data available
9.Physical and chemical properties
| Physical state | white to light yellow crystal powder |
|---|---|
| Colour | White, prismatic crystals |
| Odour | Odorless |
| Melting point/ freezing point | 234-236.5 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point or initial boiling point and boiling range | 178°C |
| Flammability | Combustible. Gives off irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. |
| Lower and upper explosion limit / flammability limit | no data available |
| Flash point | 178°C |
| Auto-ignition temperature | no data available |
| Decomposition temperature | no data available |
| pH | pH = 6.9 (1% solution) |
| Kinematic viscosity | no data available |
| Solubility | In water:20 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Partition coefficient n-octanol/water (log value) | no data available |
| Vapour pressure | 9.0X10-7 mm Hg at 25°C /Extrapolated/ |
| Density and/or relative density | 1.23 |
| Relative vapour density | no data available |
| Particle characteristics | no data available |
10.Stability and reactivity
10.1 Reactivity
no data available
10.2 Chemical stability
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
10.3 Possibility of hazardous reactions
Combustible.CAFFEINE may be hygroscopic. Aqueous solutions (1.12 mg/mL) are stable for three weeks at 5°C if protected from light. In normal room lighting and at room temperature, solutions are stable for 3 days. Solutions of this chemical in water, DMSO, 95% ethanol or acetone should be stable for 24 hours under normal lab conditions. REACTIVITY: This compound may react with strong oxidizing agents. It is also incompatible with iodine, silver salts and tannins. This compound is a very weak base. It is decomposed by strong solutions of caustic alkalis.
10.4 Conditions to avoid
no data available
10.5 Incompatible materials
no data available
10.6 Hazardous decomposition products
When heated to decomposition, it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
11.Toxicological information
Acute toxicity
- Oral: LD50 Rat oral 192 mg/kg
- Inhalation: no data available
- Dermal: no data available
Skin corrosion/irritation
no data available
Serious eye damage/irritation
no data available
Respiratory or skin sensitization
no data available
Germ cell mutagenicity
no data available
Carcinogenicity
Evaluation: There is inadequate evidence for the carcinogenicity in humans of caffeine. There is inadequate evidence for the carcinogenicity in experimental animals of caffeine. Overall evaluation: Caffeine is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans (Group 3).
Reproductive toxicity
no data available
STOT-single exposure
no data available
STOT-repeated exposure
no data available
Aspiration hazard
no data available
12.Ecological information
12.1 Toxicity
- Toxicity to fish: LC50; Species: Pimephales promelas (Fathead minnow); Conditions: freshwater, static; Concentration: 100 mg/L for 48 hr
- Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates: EC50; Species: Daphnia magna (Water flea) age < 24 hr neonate; Conditions: freshwater, static, 21°C; Concentration: 3.521 mM for 24 hr; Effect: intoxication, immobilization
- Toxicity to algae: no data available
- Toxicity to microorganisms: no data available
12.2 Persistence and degradability
AEROBIC: The estimated half-life for caffeine in the Rhine River, Netherlands, was 0.8 days, which was thought to occur as a result of biological removal processes(1). Caffeine was found to be readily biodegradable when incubated with a sewage sludge inoculum(2). Using OECD 301F method, biodegradation was found to be 58% in one vessel and 84% in a second vessel(3). The structurally analogous substance theophylline (differs by only one methyl group from caffeine) is readily biodegradable by OECD 301A method with 90-100% biodegradation after 22 days and >90% at the end of the 10-days-window(3). In biodegradation studies using 3 soils from Ontario Canada and a 34-day incubation period, 14C-caffeine was rapidly mineralized to 14-CO2 in a sandy loam and loam soil, and less rapidly in a silt loam soil(4); mineralization in the sandy loam and loam soils reached about 60% in 20 days (50% in 3-10 days) with mineralization in the silt loam soil reaching about 25% in 34 days(4). A microcosm study using sediments collected upstream and downstream from wastewater treatment plants found caffeine to undergo biomineralization under aerobic conditions(5).
12.3 Bioaccumulative potential
An estimated BCF of 3 was calculated for caffeine in fish(SRC), using a log Kow of -0.07(1) and a regression-derived equation(2). According to a classification scheme(3), this BCF suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low(SRC).
12.4 Mobility in soil
The log Koc of caffeine was experimentally determined to be 2.87 and 3.89 in a silt loam soil and in a sandy loam soil respectively(1). According to a classification scheme(2), a log Koc range of 2.87 to 3.89 (Koc range of 741 to 7762) suggests that caffeine may have low mobility in soil to being immobile in soil. Sorption tests using sand approximated a log Koc value of 1.85 (Koc of 71) using an assumed organic carbon content of 0.1% in the sand(1) which would suggest high mobility(2,SRC). Caffeine is both a weak acid and a weak base with pKa values of 14.0(3) and 0.7(4). Although partial ionization to cation and anion forms may occur, electrochemical studies have found that the neutral form of caffeine was predominant in the pH range of 5.5 to 9.0(4). Cations generally adsorb more strongly to organic carbon and clay than their neutral counterparts(5) suggesting that the cation form of caffeine may have higher Koc values than the neutral form(SRC).
12.5 Other adverse effects
no data available
13.Disposal considerations
13.1 Disposal methods
Product
The material can be disposed of by removal to a licensed chemical destruction plant or by controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Do not contaminate water, foodstuffs, feed or seed by storage or disposal. Do not discharge to sewer systems.
Contaminated packaging
Containers can be triply rinsed (or equivalent) and offered for recycling or reconditioning. Alternatively, the packaging can be punctured to make it unusable for other purposes and then be disposed of in a sanitary landfill. Controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing is possible for combustible packaging materials.
14.Transport information
14.1 UN Number
| ADR/RID: UN1544 | IMDG: UN1544 | IATA: UN1544 |
14.2 UN Proper Shipping Name
| ADR/RID: ALKALOIDS, SOLID, N.O.S. or ALKALOID SALTS, SOLID, N.O.S. |
| IMDG: ALKALOIDS, SOLID, N.O.S. or ALKALOID SALTS, SOLID, N.O.S. |
| IATA: ALKALOIDS, SOLID, N.O.S. or ALKALOID SALTS, SOLID, N.O.S. |
14.3 Transport hazard class(es)
| ADR/RID: 6.1 | IMDG: 6.1 | IATA: 6.1 |
14.4 Packing group, if applicable
| ADR/RID: III | IMDG: III | IATA: III |
14.5 Environmental hazards
| ADR/RID: no | IMDG: no | IATA: no |
14.6 Special precautions for user
no data available
14.7 Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL 73/78 and the IBC Code
no data available
15.Regulatory information
15.1 Safety, health and environmental regulations specific for the product in question
| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number |
|---|---|---|---|
| caffeine | caffeine | 58-08-2 | none |
| European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances (EINECS) | Listed. | ||
| EC Inventory | Listed. | ||
| United States Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Inventory | Listed. | ||
| China Catalog of Hazardous chemicals 2015 | Not Listed. | ||
| New Zealand Inventory of Chemicals (NZIoC) | Listed. | ||
| Philippines Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances (PICCS) | Listed. | ||
| Vietnam National Chemical Inventory | Listed. | ||
| Chinese Chemical Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances (China IECSC) | Listed. | ||
16.Other information
Information on revision
| Creation Date | Aug 18, 2017 |
|---|---|
| Revision Date | Aug 18, 2017 |
Abbreviations and acronyms
- CAS: Chemical Abstracts Service
- ADR: European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road
- RID: Regulation concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Rail
- IMDG: International Maritime Dangerous Goods
- IATA: International Air Transportation Association
- TWA: Time Weighted Average
- STEL: Short term exposure limit
- LC50: Lethal Concentration 50%
- LD50: Lethal Dose 50%
- EC50: Effective Concentration 50%
References
- IPCS - The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSC), website: http://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.home
- HSDB - Hazardous Substances Data Bank, website: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/newtoxnet/hsdb.htm
- IARC - International Agency for Research on Cancer, website: http://www.iarc.fr/
- eChemPortal - The Global Portal to Information on Chemical Substances by OECD, website: http://www.echemportal.org/echemportal/index?pageID=0&request_locale=en
- CAMEO Chemicals, website: http://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/search/simple
- ChemIDplus, website: http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
- ERG - Emergency Response Guidebook by U.S. Department of Transportation, website: http://www.phmsa.dot.gov/hazmat/library/erg
- Germany GESTIS-database on hazard substance, website: http://www.dguv.de/ifa/gestis/gestis-stoffdatenbank/index-2.jsp
- ECHA - European Chemicals Agency, website: https://echa.europa.eu/