1.Identification
1.1 GHS Product identifier
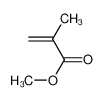
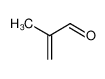
| Product name | methyl methacrylate |
|---|
1.2 Other means of identification
| Product number | - |
|---|---|
| Other names | 2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, methyl ester |
1.3 Recommended use of the chemical and restrictions on use
| Identified uses | For industry use only. Methyl methacrylate is used in the manufacture of methacrylate resins and plastics (e.g., Plexiglas). (,,,11) The principal uses of methyl methacrylate are: cast sheet and other grades (advertising signs and displays, lighting fixtures, glazing and skylights, building panels and sidings, and plumbing and bathroom fixtures), molding/extrusion powder, and coatings (latex paints, lacquer, and enamel resins). Methyl methacrylate is used in the impregnation of concrete to make it water-repellent, and also has uses in the fields of medicine and dentistry to make prosthetic devices and as a ceramic filler or cement. |
|---|---|
| Uses advised against | no data available |
1.4 Supplier's details
| Company | MOLBASE (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
|---|---|
| Address | Floor 4 & 5, Building 12, No. 1001 North Qinzhou Road, Xuhui District, Shanghai, China |
| Telephone | +86(21)64956998 |
| Fax | +86(21)54365166 |
1.5 Emergency phone number
| Emergency phone number | +86-400-6021-666 |
|---|---|
| Service hours | Monday to Friday, 9am-5pm (Standard time zone: UTC/GMT +8 hours). |
2.Hazard identification
2.1 Classification of the substance or mixture
Flammable liquids, Category 2
Skin irritation, Category 2
Skin sensitization, Category 1
Specific target organ toxicity – single exposure, Category 3
2.2 GHS label elements, including precautionary statements
| Pictogram(s) |   |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statement(s) | H225 Highly flammable liquid and vapour H315 Causes skin irritation H317 May cause an allergic skin reaction H335 May cause respiratory irritation |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| Prevention | P210 Keep away from heat, hot surfaces, sparks, open flames and other ignition sources. No smoking. P233 Keep container tightly closed. P240 Ground and bond container and receiving equipment. P241 Use explosion-proof [electrical/ventilating/lighting/...] equipment. P242 Use non-sparking tools. P243 Take action to prevent static discharges. P280 Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P264 Wash ... thoroughly after handling. P261 Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272 Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P271 Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. |
| Response | P303+P361+P353 IF ON SKIN (or hair): Take off immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse skin with water [or shower]. P370+P378 In case of fire: Use ... to extinguish. P302+P352 IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of water/... P321 Specific treatment (see ... on this label). P332+P313 If skin irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P362+P364 Take off contaminated clothing and wash it before reuse. P333+P313 If skin irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P304+P340 IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing. P312 Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/…if you feel unwell. |
| Storage | P403+P235 Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep cool. P403+P233 Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. P405 Store locked up. |
| Disposal | P501 Dispose of contents/container to ... |
2.3 Other hazards which do not result in classification
none
3.Composition/information on ingredients
3.1 Substances
| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| methyl methacrylate | methyl methacrylate | 80-62-6 | none | 100% |
4.First-aid measures
4.1 Description of necessary first-aid measures
General advice
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaled
Fresh air, rest. Refer for medical attention.
In case of skin contact
Remove contaminated clothes. Rinse and then wash skin with water and soap.
In case of eye contact
First rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention.
If swallowed
Rinse mouth. Give one or two glasses of water to drink. Refer for medical attention .
4.2 Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayed
Irritation of eyes, nose, and throat. Nausea and vomiting. Liquid may cause skin irritation. (USCG, 1999)
4.3 Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed, if necessary
Immediate first aid: Ensure that adequate decontamination has been carried out. If patient is not breathing, start artificial respiration, preferably with a demand-valve resuscitator, bag-valve-mask device, or pocket mask, as trained. Perform CPR as necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep patient quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Esters and related compounds/
5.Fire-fighting measures
5.1 Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
Use dry chemical, carbon dioxide, or foam extinguishers. Vapors are heavier than air and will collect in low areas. Vapors may travel long distances to ignition sources and flashback. Vapors in confined areas may explode when exposed to fire. Containers may explode in fire. Storage containers and parts of containers may rocket great distances, in many directions. If material or contaminated runoff enters waterways, notify downstream users of potentially contaminated waters. Notify local health and fire officials and pollution control agencies. From a secure, explosion-proof location, use water spray to cool exposed containers. If cooling streams are ineffective (venting sound increases in volume and pitch, tank discolors or shows any signs of deforming), withdraw immediately to a secure position.
5.2 Specific hazards arising from the chemical
Behavior in Fire: Vapor is heavier than air and may travel a considerable distance to a source of ignition and flash back. Containers may explode in fire or when heated because of polymerization. (USCG, 1999)
5.3 Special protective actions for fire-fighters
Wear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
6.Accidental release measures
6.1 Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust. For personal protection see section 8.
6.2 Environmental precautions
Personal protection: chemical protection suit and filter respirator for organic gases and vapours adapted to the airborne concentration of the substance. Remove all ignition sources. Do NOT wash away into sewer. Collect leaking and spilled liquid in sealable containers as far as possible. Absorb remaining liquid in sand or inert absorbent. Then store and dispose of according to local regulations.
6.3 Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
SRP: Wastewater from contaminant suppression, cleaning of protective clothing/equipment, or contaminated sites should be contained and evaluated for subject chemical or decomposition product concentrations. Concentrations shall be lower than applicable environmental discharge or disposal criteria. Alternatively, pretreatment and/or discharge to a permitted wastewater treatment facility is acceptable only after review by the governing authority and assurance that "pass through" violations will not occur. Due consideration shall be given to remediation worker exposure (inhalation, dermal and ingestion) as well as fate during treatment, transfer and disposal. If it is not practicable to manage the chemical in this fashion, it must be evaluated in accordance with EPA 40 CFR Part 261, specifically Subpart B, in order to determine the appropriate local, state and federal requirements for disposal.
7.Handling and storage
7.1 Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. For precautions see section 2.2.
7.2 Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Fireproof. Separated from strong oxidants, strong bases and strong acids. Cool. Keep in the dark. Keep in a well-ventilated room. Store only if stabilized.Before entering confined space where this chemical may be present, check to make sure that an explosive concentration does not exist. Methyl methacrylate must be stored to avoid contact with oxidizers, such as nitrates, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorates, and peroxides; strong alkalis, such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, and strong acids, such as nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and sulfuric acid, since violent reactions occur. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well ventilated area away from light, heat, and ionizing radiation, because methyl methacrylate will react and release heat quickly causing an explosion. Store with an appropriate inhibitor. Lack of an appropriate inhibitor may cause an explosive reaction.
8.Exposure controls/personal protection
8.1 Control parameters
Occupational Exposure limit values
Recommended Exposure Limit: 10 hr Time-Weighted avg: 100 ppm (410 mg/cu m).
Biological limit values
no data available
8.2 Appropriate engineering controls
Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
8.3 Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE)
Eye/face protection
Safety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Wear impervious clothing. The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace. Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Respiratory protection
Wear dust mask when handling large quantities.
Thermal hazards
no data available
9.Physical and chemical properties
| Physical state | COLOURLESS LIQUID |
|---|---|
| Colour | Colorless volatile liquid |
| Odour | Characteristic quality: sulfur-like, sweet, sharp; hedonic tone: unpleasant |
| Melting point/ freezing point | 162°C(lit.) |
| Boiling point or initial boiling point and boiling range | 100°C |
| Flammability | Class IB Flammable Liquid: Fl.P. below 22.78°C and BP at or above 37.78°C.Highly flammable. |
| Lower and upper explosion limit / flammability limit | Lower 1.7%; Upper 8.2% (by volume) |
| Flash point | 9°C(lit.) |
| Auto-ignition temperature | 421.11°C (USCG, 1999) |
| Decomposition temperature | no data available |
| pH | no data available |
| Kinematic viscosity | no data available |
| Solubility | 1 to 10 mg/mL at 17.5°C |
| Partition coefficient n-octanol/water (log value) | log Kow = 1.38 |
| Vapour pressure | 40 mm Hg at 25.5°C |
| Density and/or relative density | 0.943 |
| Relative vapour density | 3.45 (Relative to Air) |
| Particle characteristics | no data available |
10.Stability and reactivity
10.1 Reactivity
no data available
10.2 Chemical stability
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
10.3 Possibility of hazardous reactions
A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame ...The vapour mixes well with air, explosive mixtures are easily formed. Vapours are uninhibited and may polymerize, causing blockage of vents.METHYL METHACRYLATE MONOMER, may polymerize if contaminated or subjected to heat. If polymerization takes place in a container, the container is subject to violent rupture. Oxidizes readily in air to form unstable peroxides that may explode spontaneously [Bretherick 1979. p.151-154, 164]. Peroxides may also initiate exothermic polymierization of the bulk material [Bretherick 1979. p. 160]. Benzoyl peroxide was weighed into a beaker that had previously been rinsed with methyl methacrylate. The peroxide catalyzed polymerization of the methyl methacrylate and the build-up of heat ignited the remaining peroxide [MCA Case History 996. 1964].
10.4 Conditions to avoid
no data available
10.5 Incompatible materials
... Can react with oxidizing materials.
10.6 Hazardous decomposition products
When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
11.Toxicological information
Acute toxicity
- Oral: LD50 Rat oral 9400 mg/kg.
- Inhalation: LC50 Rat inhalation 11,250 - 12,500 ppm/2 hr
- Dermal: no data available
Skin corrosion/irritation
no data available
Serious eye damage/irritation
no data available
Respiratory or skin sensitization
no data available
Germ cell mutagenicity
no data available
Carcinogenicity
Evaluation: There is inadequate evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of methyl methacrylate. There is evidence suggesting lack of carcinogenicity of methyl methacrylate in experimental animals. Overall evaluation: Methyl methacrylate is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans (Group3).
Reproductive toxicity
No adequate reproductive or developmental studies in humans are available. Inhalation exposure of rats to maternally-toxic levels of methyl methacrylate resulted in fetal abnormalities (hematomas and skeletal anomalies) and decreased fetal weight and crown-rump length.
STOT-single exposure
no data available
STOT-repeated exposure
no data available
Aspiration hazard
no data available
12.Ecological information
12.1 Toxicity
- Toxicity to fish: LC50; Species: Lepomis macrochirus (Bluegill, juvenile, length 3.65 cm, weight 0.90 g); Conditions: freshwater, flow through, 22°C, pH 6-8, dissolved oxygen >7.5 mg/L; Concentration: 420 mg/L for 1 hr /practical grade
- Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates: LC50; Species: Daphnia magna (Water flea, age < or =24 hr); Conditions: freshwater, static, 20-22°C, pH 7.6-7.7; Concentration: 1760 mg/L for 24 hr /formulation
- Toxicity to algae: no data available
- Toxicity to microorganisms: no data available
12.2 Persistence and degradability
AEROBIC: Methyl methacrylate, present at 100 mg/L, reached 94% of its theoretical BOD in 2 weeks using an activated sludge inoculum in the Japanese MITI test(1). In the modified Japanese MITI test, methyl methacrylate reached 32% of its theoretical BOD after 28 days; in a closed bottle test, methyl methacrylate released 88% of carbon dioxide evolution after 28 days; and >95% methyl methacrylate was degraded in the Zahn-Wellens test, time not specified(2). Methyl methacrylate was reported to be completely degraded by activated sludge in approximately 20 hours(3). In a standard biodegradability test using sewage seed, 42% of the theoretical BOD was consumed in 19 days, including a 3-4 day lag period; with acclimated seed, 66% of the theoretical BOD was consumed in 22 days(4). The biodegradation rate for methyl methacrylate at 75 ppm starting concentration, treated using a mixed microbial population immobilized in calcium alginate gel, was 9.3 ppm/hr; this corresponded to 89% removal due to biodegradation(5).
12.3 Bioaccumulative potential
An estimated BCF of 4 was calculated in fish for methyl methacrylate(SRC), using a log Kow of 1.38(1) and a regression-derived equation(2). According to a classification scheme(3), this BCF suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low(SRC).
12.4 Mobility in soil
The Koc of methyl methacrylate has been measured as 9-72(1) and as high as 95(2). According to a classification scheme(3), this Koc range suggests that methyl methacrylate is expected to have very high to high mobility in soil.
12.5 Other adverse effects
no data available
13.Disposal considerations
13.1 Disposal methods
Product
The material can be disposed of by removal to a licensed chemical destruction plant or by controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Do not contaminate water, foodstuffs, feed or seed by storage or disposal. Do not discharge to sewer systems.
Contaminated packaging
Containers can be triply rinsed (or equivalent) and offered for recycling or reconditioning. Alternatively, the packaging can be punctured to make it unusable for other purposes and then be disposed of in a sanitary landfill. Controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing is possible for combustible packaging materials.
14.Transport information
14.1 UN Number
| ADR/RID: UN1247 | IMDG: UN1247 | IATA: UN1247 |
14.2 UN Proper Shipping Name
| ADR/RID: METHYL METHACRYLATE MONOMER, STABILIZED |
| IMDG: METHYL METHACRYLATE MONOMER, STABILIZED |
| IATA: METHYL METHACRYLATE MONOMER, STABILIZED |
14.3 Transport hazard class(es)
| ADR/RID: 3 | IMDG: 3 | IATA: 3 |
14.4 Packing group, if applicable
| ADR/RID: II | IMDG: II | IATA: II |
14.5 Environmental hazards
| ADR/RID: no | IMDG: no | IATA: no |
14.6 Special precautions for user
no data available
14.7 Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL 73/78 and the IBC Code
no data available
15.Regulatory information
15.1 Safety, health and environmental regulations specific for the product in question
| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number |
|---|---|---|---|
| methyl methacrylate | methyl methacrylate | 80-62-6 | none |
| European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances (EINECS) | Listed. | ||
| EC Inventory | Listed. | ||
| United States Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Inventory | Listed. | ||
| China Catalog of Hazardous chemicals 2015 | Listed. | ||
| New Zealand Inventory of Chemicals (NZIoC) | Listed. | ||
| Philippines Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances (PICCS) | Listed. | ||
| Vietnam National Chemical Inventory | Listed. | ||
| Chinese Chemical Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances (China IECSC) | Listed. | ||
16.Other information
Information on revision
| Creation Date | Aug 12, 2017 |
|---|---|
| Revision Date | Aug 12, 2017 |
Abbreviations and acronyms
- CAS: Chemical Abstracts Service
- ADR: European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road
- RID: Regulation concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Rail
- IMDG: International Maritime Dangerous Goods
- IATA: International Air Transportation Association
- TWA: Time Weighted Average
- STEL: Short term exposure limit
- LC50: Lethal Concentration 50%
- LD50: Lethal Dose 50%
- EC50: Effective Concentration 50%
References
- IPCS - The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSC), website: http://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.home
- HSDB - Hazardous Substances Data Bank, website: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/newtoxnet/hsdb.htm
- IARC - International Agency for Research on Cancer, website: http://www.iarc.fr/
- eChemPortal - The Global Portal to Information on Chemical Substances by OECD, website: http://www.echemportal.org/echemportal/index?pageID=0&request_locale=en
- CAMEO Chemicals, website: http://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/search/simple
- ChemIDplus, website: http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
- ERG - Emergency Response Guidebook by U.S. Department of Transportation, website: http://www.phmsa.dot.gov/hazmat/library/erg
- Germany GESTIS-database on hazard substance, website: http://www.dguv.de/ifa/gestis/gestis-stoffdatenbank/index-2.jsp
- ECHA - European Chemicals Agency, website: https://echa.europa.eu/






-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
More Suppliers>>Hangzhou J&H Chemical Co., Ltd.
CHINA
Purity: 98%
Lead Time: 7 Day(s)
Price: -
Xiamen Zhixin Chemical Co., Ltd.
CHINA
Purity: 99%
Lead Time: 3 Day(s)
Price: -
CHINA
Purity: 99%
Lead Time: 14 Day(s)
Price: -
Henan Coreychem Co.,Ltd
CHINA
Purity: 98%
Lead Time: 3 Day(s)
Price: -
Hangzhou DayangChem Co., Ltd
CHINA
Purity: 98%
Lead Time: 7 Day(s)
Price: -
Skyrun Industrial Co., Limited
CHINA
Purity: 99%
Lead Time: 7 Day(s)
Price: -
Hangzhou Bingochem Co., Ltd.
CHINA
Purity: 98%
Lead Time: 7 Day(s)
Price: -
Shanghai Synchem Pharma Co., Ltd
CHINA
Purity: %
Lead Time: Day(s)
Price: -
CHINA
Purity: 99%
Lead Time: 1 Day(s)
Price: Min $10 /kg
CHINA
Purity: 99.8%
Lead Time: 0 Day(s)
Price: Min $1.8 /kg