1.Identification
1.1 GHS Product identifier
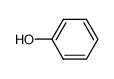
| Product name | phenol |
|---|
1.2 Other means of identification
| Product number | - |
|---|---|
| Other names | PHENOL |
1.3 Recommended use of the chemical and restrictions on use
| Identified uses | For industry use only. Phenols/phenoxy acids |
|---|---|
| Uses advised against | no data available |
1.4 Supplier's details
| Company | MOLBASE (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
|---|---|
| Address | Floor 4 & 5, Building 12, No. 1001 North Qinzhou Road, Xuhui District, Shanghai, China |
| Telephone | +86(21)64956998 |
| Fax | +86(21)54365166 |
1.5 Emergency phone number
| Emergency phone number | +86-400-6021-666 |
|---|---|
| Service hours | Monday to Friday, 9am-5pm (Standard time zone: UTC/GMT +8 hours). |
2.Hazard identification
2.1 Classification of the substance or mixture
Acute toxicity - Oral, Category 3
Acute toxicity - Dermal, Category 3
Skin corrosion, Category 1B
Acute toxicity - Inhalation, Category 3
Germ cell mutagenicity, Category 2
Specific target organ toxicity – repeated exposure, Category 2
2.2 GHS label elements, including precautionary statements
| Pictogram(s) |  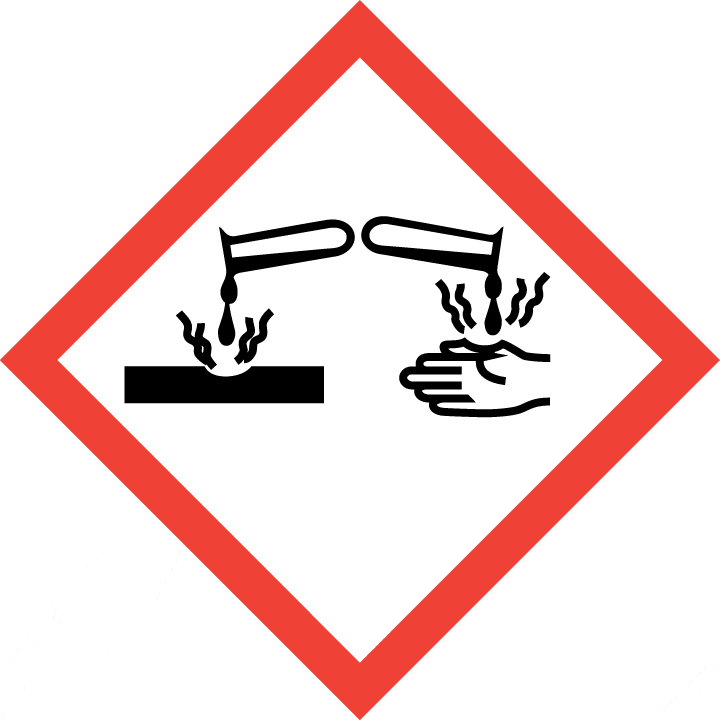  |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statement(s) | H301 Toxic if swallowed H311 Toxic in contact with skin H314 Causes severe skin burns and eye damage H331 Toxic if inhaled H341 Suspected of causing genetic defects |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| Prevention | P264 Wash ... thoroughly after handling. P270 Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280 Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P260 Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P261 Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271 Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P201 Obtain special instructions before use. P202 Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. |
| Response | P301+P310 IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/… P321 Specific treatment (see ... on this label). P330 Rinse mouth. P302+P352 IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of water/... P312 Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/…if you feel unwell. P361+P364 Take off immediately all contaminated clothing and wash it before reuse. P301+P330+P331 IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353 IF ON SKIN (or hair): Take off immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse skin with water [or shower]. P363 Wash contaminated clothing before reuse. P304+P340 IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing. P310 Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/… P305+P351+P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. P311 Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/… P308+P313 IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/ attention. P314 Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. |
| Storage | P405 Store locked up. P403+P233 Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
| Disposal | P501 Dispose of contents/container to ... |
2.3 Other hazards which do not result in classification
none
3.Composition/information on ingredients
3.1 Substances
| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| phenol | phenol | 108-95-2 | none | 100% |
4.First-aid measures
4.1 Description of necessary first-aid measures
General advice
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaled
Fresh air, rest. Half-upright position. Refer for medical attention.
In case of skin contact
Remove contaminated clothes. Rinse skin with plenty of water or shower. To remove substance use polyethylene glycol 300 or vegetable oil. Refer for medical attention . Wear protective gloves when administering first aid.
In case of eye contact
First rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention.
If swallowed
Rinse mouth. Give one or two glasses of water to drink. Do NOT induce vomiting. Refer for medical attention .
4.2 Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayed
Excerpt from ERG Guide 153 [Substances - Toxic and/or Corrosive (Combustible)]: TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution. (ERG, 2016)
Will burn eyes and skin. The analgesic action may cause loss of pain sensation. Readily absorbed through skin, causing increased heart rate, convulsions, and death. (USCG, 1999)
Excerpt from ERG Guide 153 [Substances - Toxic and/or Corrosive (Combustible)]: TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution. (ERG, 2016)
Toxic hazard rating is very toxic: probable oral lethal dose (human) is 50-500 mg/kg. Ingestion of 1 gram has been lethal to humans. Lethal amounts may be absorbed through skin or inhaled. Industrial contact can cause chronic poisoning with kidney and liver damage. Persons affected with hepatic or kidney diseases are at a greater risk. (EPA, 1998)
4.3 Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed, if necessary
Because of the rapid onset of symptoms, possible increased phenol absorption with dilution, and the potential for development of seizures, activated charcoal (1 g/kg) is preferable to lavage or syrup of ipecac. In vitro studies indicated that activated charcoal efficiently absorbs phenol. A cathartic should be given after oral activated charcoal.
5.Fire-fighting measures
5.1 Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
If material on fire or involved in fire: Use water in flooding quantities as fog. Solid streams of water may be ineffective. Cool all affected containers with flooding quantities of water. Apply water from as far a distance as possible. Use foam, dry chemical, or carbon dioxide. Keep run off-water out of sewers and water sources. /Phenol, solid/
5.2 Specific hazards arising from the chemical
Excerpt from ERG Guide 153 [Substances - Toxic and/or Corrosive (Combustible)]: Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Those substances designated with a (P) may polymerize explosively when heated or involved in a fire. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form. (ERG, 2016)
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Unburned vapor is toxic Behavior in Fire: Yields flammable vapors when heated, which will form explosive mixtures with air (USCG, 1999)
Excerpt from ERG Guide 153 [Substances - Toxic and/or Corrosive (Combustible)]: Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Those substances designated with a (P) may polymerize explosively when heated or involved in a fire. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form. (ERG, 2016)
Flammable vapors when heated. Runoff from fire control water may give off poisonous gases and cause pollution. Mixtures of 9-10% phenol in air are explosive. Avoid aluminum chloride/nitrobenzene mixture, peroxodisulfuric acid, peroxomonosulfuric acid and strong oxidizing agents. Decomposes slowly on air contact. Avoid contact with strong oxidizing agents. (EPA, 1998)
5.3 Special protective actions for fire-fighters
Wear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
6.Accidental release measures
6.1 Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust. For personal protection see section 8.
6.2 Environmental precautions
Personal protection: complete protective clothing including self-contained breathing apparatus. Do NOT let this chemical enter the environment. Sweep spilled substance into covered sealable containers. If appropriate, moisten first to prevent dusting. Carefully collect remainder. Then store and dispose of according to local regulations.
6.3 Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
Control runoff and isolate discharged material for proper disposal. Approach release from upwind.
7.Handling and storage
7.1 Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. For precautions see section 2.2.
7.2 Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Provision to contain effluent from fire extinguishing. Separated from strong oxidants and food and feedstuffs. Dry. Well closed. Keep in a well-ventilated room.Phenol should be stored in closed containers in an area which is adequate to ensure that airborne phenol concentrations do not exceed 20 mg/cu m. Conditions shall be controlled to prevent overheating and the buildup of pressure in phenol containers. Storage tanks must be electrically grounded and bonded to transfer lines. Transfer and storage systems shall be designed and operated to prevent blockage by condensed phenol. Open flames are prohibited when drums of phenol are heated to melt the contents. The internal pressure will be vented by placing the drums with the bung up and the bung loosened. The bungs shall be tightened prior to moving or handling drums. Drums, carboys, or other containers of phenol shall be closed while being handled or moved. Transfer from such containers shall be done carefully to avoid splashes, spills, or other possible circumstances by which an employee may come in contact with phenol. Bulk storage facilities shall be designed and constructed to contain any leaks or spills.
8.Exposure controls/personal protection
8.1 Control parameters
Occupational Exposure limit values
Recommended Exposure Limit: 15 Min Ceiling Value: 15.6 ppm (60 mg/cu m), skin.
Recommended Exposure Limit: 10 Hr Time-Weighted Avg: 5 ppm (19 mg/cu m).
Biological limit values
no data available
8.2 Appropriate engineering controls
Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
8.3 Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE)
Eye/face protection
Safety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Wear impervious clothing. The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace. Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Respiratory protection
Wear dust mask when handling large quantities.
Thermal hazards
no data available
9.Physical and chemical properties
| Physical state | transparent crystalline solid |
|---|---|
| Colour | Colorless acicular crystals or white, crystalline mass |
| Odour | Distinct aromatic, somewhat sickening sweet and acrid odor, discernable at 0.5 to 5 ppm |
| Melting point/ freezing point | 236°C(dec.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point or initial boiling point and boiling range | 182°C(lit.) |
| Flammability | Combustible SolidCombustible. |
| Lower and upper explosion limit / flammability limit | 1.7%-8.6% IN AIR |
| Flash point | 79°C |
| Auto-ignition temperature | 715°C |
| Decomposition temperature | no data available |
| pH | about 6.0 (aq soln) |
| Kinematic viscosity | 3.437 mPa s @ 50°C; 1.784 mPa s @ 75°C; 1.099 mPa s @ 100°C |
| Solubility | In water:8 g/100 mL |
| Partition coefficient n-octanol/water (log value) | no data available |
| Vapour pressure | 0.09 psi ( 55 °C) |
| Density and/or relative density | 1.071g/mLat 25°C(lit.) |
| Relative vapour density | 3.24 (vs air) |
| Particle characteristics | no data available |
10.Stability and reactivity
10.1 Reactivity
no data available
10.2 Chemical stability
Prone to redden on exposure to air and light, hastened by presence of alkalinity.
10.3 Possibility of hazardous reactions
May be ignited by electrostatic discharge.Phenols do not behave as organic alcohols, as one might guess from the presence of a hydroxyl (-OH) group in their structure. Instead, they react as weak organic acids. Phenols and cresols are much weaker as acids than common carboxylic acids (phenol has pKa = 9.88). These materials are incompatible with strong reducing substances such as hydrides, nitrides, alkali metals, and sulfides. Flammable gas (H2) is often generated, and the heat of the reaction may ignite the gas. Heat is also generated by the acid-base reaction between phenols and bases. Such heating may initiate polymerization of the organic compound. Phenols are sulfonated very readily (for example, by concentrated sulfuric acid at room temperature). The reactions generate heat. Phenols are also nitrated very rapidly, even by dilute nitric acid. Phenol may explode in contact with peroxodisulfuric acid (D'Ans, J. Ber., 1910, 43, 1880; Z. Anorg. Chem., 1911, 73, 1911.) or peroxomonosulfuric acid. (Sidgwick, 1950, 939)
10.4 Conditions to avoid
no data available
10.5 Incompatible materials
Addition of aluminum chloride to a large volume of recovered nitrobenzene containing 5% phenol caused a violent explosion. Experiment showed that mixtures containing all three components reacted violently at 120°C.
10.6 Hazardous decomposition products
When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
11.Toxicological information
Acute toxicity
- Oral: LD50 Rat oral 530 mg/kg
- Inhalation: no data available
- Dermal: no data available
Skin corrosion/irritation
no data available
Serious eye damage/irritation
no data available
Respiratory or skin sensitization
no data available
Germ cell mutagenicity
no data available
Carcinogenicity
Evaluation: There is inadequate evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of phenol. There is inadequate evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of phenol. Overall evaluation: Phenol is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans (Group 3).
Reproductive toxicity
no data available
STOT-single exposure
no data available
STOT-repeated exposure
no data available
Aspiration hazard
no data available
12.Ecological information
12.1 Toxicity
- Toxicity to fish: LC50 Lepomis macrochirus >10; >15 mg/l/24-48 hr /Conditions of bioassay not specified
- Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates: LC50 Daphnia magna (young) 17 mg/l/24-48 hr /Conditions of bioassay not specified
- Toxicity to algae: no data available
- Toxicity to microorganisms: no data available
12.2 Persistence and degradability
AEROBIC: Phenol is a benchmark chemical in screening tests and there is abundant data to indicate that phenol biodegrades fast in aerobic screening tests using a variety of techniques and inocula, including acclimated and unacclimated activated sludge, sewage, and soil(SRC). Only selected results are included here (SRC). In a 2-week biodegradation screening test (MITI test) using phenol (100 mg/l) and an activated sludge inoculum, 85% of theoretical BOD was removed(1). Phenol was completely removed in 1 day or less using a soil suspension(2) or activated sludge inocula(3,6). Complete degradation was observed in 4 days using sediment from an oil refinery settling pond as an inoculum(4). It was shown that the presence of aromatic compounds like benzene and naphthalene had a mild inhibitory effect on degradation(4). In five days, the BOD consumed was 90% and 50% of theoretical using a sewage inoculum and freshwater and seawater, respectively(5). Another investigator who obtained 80% of theoretical BOD consumed after 5 days demonstrated that adaptation of the inoculum has a marked effect on the biodegradation rate(8). Decreasing the concn of phenol significantly reduces the lag time required to initiate degradation and increases the removal rate(9). The maximum mineralization rates of phenol in sewage and landfill leachate were 6.5X10-4 and 2.7X10-4 hr-1, respectively(7). A lag period was observed in landfill leachate(7).
12.3 Bioaccumulative potential
The BCFs reported in fish include: Goldorfe, 20 (1); goldfish, (Carassius auratus), 1.9(2); fish (unspecified), 17(3); fish (unspecified), 1.7(4); and 39, rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) (5). Phenol was rapidly eliminated from goldfish(6) and therefore would be unlikely to bioaccumulate(SRC). When U-14C-phenol was interperitonially administered to goldfish, the concn decreased to one tenth the initial concn in 2 hr(6). A BCF of 15,800 was reported in fathead minnows using 14C labeled phenol(7). Minor amounts of 14C in tissues were present as parent compound after 28 days of exposure to radiolabeled phenol(7). Parent compound comprised 1.5% of total 14C as phenol after 28 days of depuration(7). According to a classification scheme(8), reported BCF values and the rapid elimination of phenol suggests that bioaccumulation of phenol is unlikely(SRC). According to a classification scheme, BCF values <30 are low and from 100 or greater are high(8).
12.4 Mobility in soil
Phenol is reported to have low adsorptivity to clay soils and silt loam(1) and no adsorption to aquifer material(3) and montmorillonite and kaolinite clays(8). The Koc for phenol to a Batcombe silt loam soil (pH 6.7, organic carbon 2.51%) was 30(6). It was 16 for a Brookstone clay loam (pH 5.7, organic matter 5.1%) and varied with pH and iron content of the soil(7). The Freundlich K and (1/N) for phenol in Captina (pH 5.7, 1.1 % organic matter) and Palouse silt loam (pH 5.7, 3.6% organic matter) soils were 0.58 (1.15) and 0.81 (1.00)(2); the Koc values for these soils are 91 and 39(SRC). Based on the reported Koc values, phenol would be expected to generally exhibit very high mobility in soil, based on a classification scheme(4). In a study of the adsorption of phenol onto siltstone associated with a Wyoming coal deposit suitable for in situ gasification, the pH of the solution was the major controlling factor with adsorption occurring at pH's below the pKa of phenol and no adsorption occurring at pH's above the pKa(5). The log of the Freundlich K value was approximately -4(5). Therefore, phenol may be transported by groundwater near in situ coal gasification sites due to the elevated pH's at these sites after gasification(5). The pKa of phenol is 9.99(9), indicating that it will be partially dissociated at the upper end of environmental pH range and its mobility may be pH dependent(SRC). In general, anions generally do not adsorb to organic carbon and clay as strongly as their neutral counterparts(10).
12.5 Other adverse effects
no data available
13.Disposal considerations
13.1 Disposal methods
Product
The material can be disposed of by removal to a licensed chemical destruction plant or by controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Do not contaminate water, foodstuffs, feed or seed by storage or disposal. Do not discharge to sewer systems.
Contaminated packaging
Containers can be triply rinsed (or equivalent) and offered for recycling or reconditioning. Alternatively, the packaging can be punctured to make it unusable for other purposes and then be disposed of in a sanitary landfill. Controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing is possible for combustible packaging materials.
14.Transport information
14.1 UN Number
| ADR/RID: UN1671 | IMDG: UN1671 | IATA: UN1671 |
14.2 UN Proper Shipping Name
| ADR/RID: PHENOL, SOLID |
| IMDG: PHENOL, SOLID |
| IATA: PHENOL, SOLID |
14.3 Transport hazard class(es)
| ADR/RID: 6.1 | IMDG: 6.1 | IATA: 6.1 |
14.4 Packing group, if applicable
| ADR/RID: II | IMDG: II | IATA: II |
14.5 Environmental hazards
| ADR/RID: no | IMDG: no | IATA: no |
14.6 Special precautions for user
no data available
14.7 Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL 73/78 and the IBC Code
no data available
15.Regulatory information
15.1 Safety, health and environmental regulations specific for the product in question
| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number |
|---|---|---|---|
| phenol | phenol | 108-95-2 | none |
| European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances (EINECS) | Listed. | ||
| EC Inventory | Listed. | ||
| United States Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Inventory | Listed. | ||
| China Catalog of Hazardous chemicals 2015 | Listed. | ||
| New Zealand Inventory of Chemicals (NZIoC) | Listed. | ||
| Philippines Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances (PICCS) | Listed. | ||
| Vietnam National Chemical Inventory | Listed. | ||
| Chinese Chemical Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances (China IECSC) | Listed. | ||
16.Other information
Information on revision
| Creation Date | Aug 10, 2017 |
|---|---|
| Revision Date | Aug 10, 2017 |
Abbreviations and acronyms
- CAS: Chemical Abstracts Service
- ADR: European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road
- RID: Regulation concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Rail
- IMDG: International Maritime Dangerous Goods
- IATA: International Air Transportation Association
- TWA: Time Weighted Average
- STEL: Short term exposure limit
- LC50: Lethal Concentration 50%
- LD50: Lethal Dose 50%
- EC50: Effective Concentration 50%
References
- IPCS - The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSC), website: http://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.home
- HSDB - Hazardous Substances Data Bank, website: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/newtoxnet/hsdb.htm
- IARC - International Agency for Research on Cancer, website: http://www.iarc.fr/
- eChemPortal - The Global Portal to Information on Chemical Substances by OECD, website: http://www.echemportal.org/echemportal/index?pageID=0&request_locale=en
- CAMEO Chemicals, website: http://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/search/simple
- ChemIDplus, website: http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
- ERG - Emergency Response Guidebook by U.S. Department of Transportation, website: http://www.phmsa.dot.gov/hazmat/library/erg
- Germany GESTIS-database on hazard substance, website: http://www.dguv.de/ifa/gestis/gestis-stoffdatenbank/index-2.jsp
- ECHA - European Chemicals Agency, website: https://echa.europa.eu/








-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
-
-

-
More Suppliers>>Nanjing Yushan Chemical Co., Ltd.
CHINA
Purity: 98%
Lead Time: 3 Week(s)
Price: Min $600 /g
Baoji Guokang Bio-Technology Co., Ltd
CHINA
Purity: 99%
Lead Time: 3 Day(s)
Price: -
Nanjing Yushan Chemical Co., Ltd.
CHINA
Purity: 99.99%
Lead Time: 1 Week(s)
Price: Min $7700 /吨
Wenzhou Win-Win Chemical Co., Ltd.
CHINA
Purity: 98%
Lead Time: 1 Week(s)
Price: -
Hangzhou J&H Chemical Co., Ltd.
CHINA
Purity: 99.99%
Lead Time: 1 Week(s)
Price: -
Hangzhou J&H Chemical Co., Ltd.
CHINA
Purity: >97%
Lead Time: 7 Day(s)
Price: -
Xiamen Zhixin Chemical Co., Ltd.
CHINA
Purity: 99%
Lead Time: 3 Day(s)
Price: -
Skyrun Industrial Co., Limited
CHINA
Purity: 99%
Lead Time: 7 Day(s)
Price: -
Henan Coreychem Co.,Ltd
CHINA
Purity: 99.99%
Lead Time: 3 Day(s)
Price: -
CHINA
Purity: 99.99%
Lead Time: 1 Week(s)
Price: Min $7700 /吨